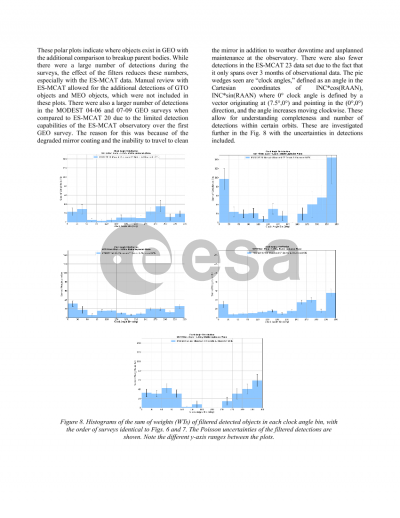
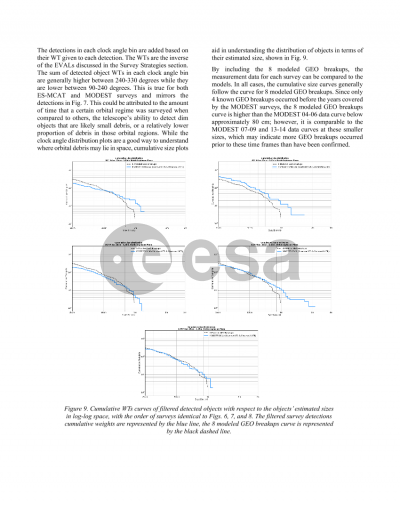
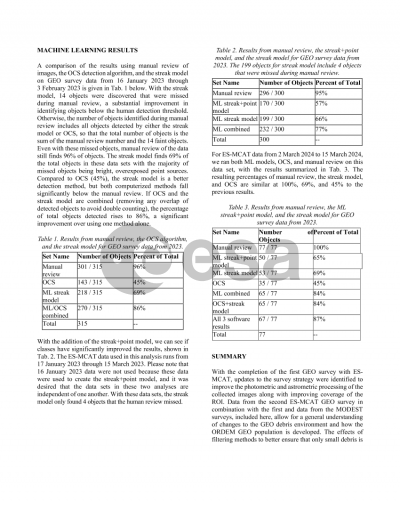
Document details

Abstract
The Eugene Stansbery-Meter Class Autonomous Telescope (ES-MCAT) is NASA’s primary sensor for surveying small debris in geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO) and provides data for updating the NASA Orbital Debris Engineering Model (ORDEM). Data from 2020 to 2023 have been analyzed for use in supporting ORDEM 4.0 development. This ES-MCAT dataset was compared with previously collected GEO survey data that used the Michigan Orbital DEbris Survey Telescope (MODEST) to assess the evolving orbital debris environment and new insights that could be gained with updated survey methods and analysis techniques.
New methodologies in filtering detected objects for all GEO surveys and refinements of previous GEO breakup knowledge were investigated. The historical data are further compared to 2023 data analyzed using various detection techniques, including the introduction of machine learning (ML) to help detect orbital debris in optical images. The ML model uses the "You Only Look Once" version 9 (YOLO-v9) architecture and was trained on both simulated objects and objects detected during the 2023 GEO survey. This model improves detection completeness for faint and trailed objects when compared to previous software models. Nevertheless, limitations exist when dealing with a larger variety of object morphologies in astronomical images. Combining the previous software’s detections with the new ML model increases the overall detection rate, including detecting objects too faint to be detected during manual review of data.
This paper presents an overview of the ES-MCAT GEO survey strategies; a comparison of data collected with ES-MCAT and MODEST; and the results of different detection methods, including manual review and ML. Applications to building and validating ORDEM are also discussed.
Preview