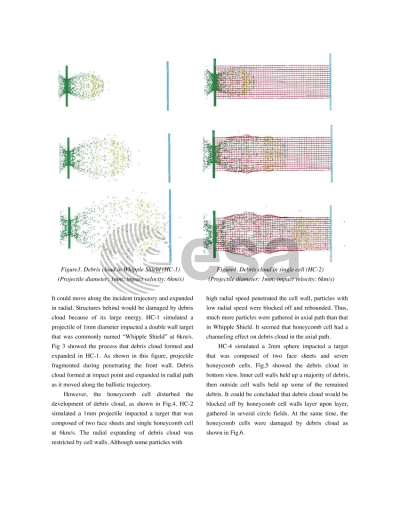
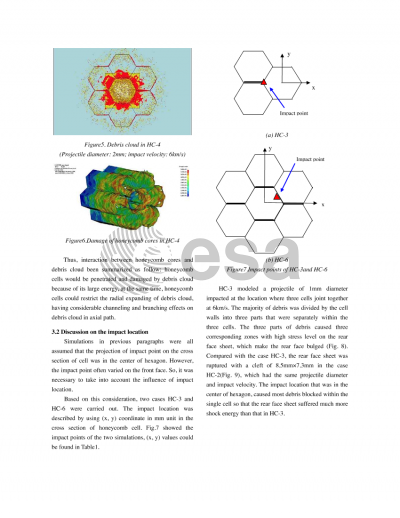
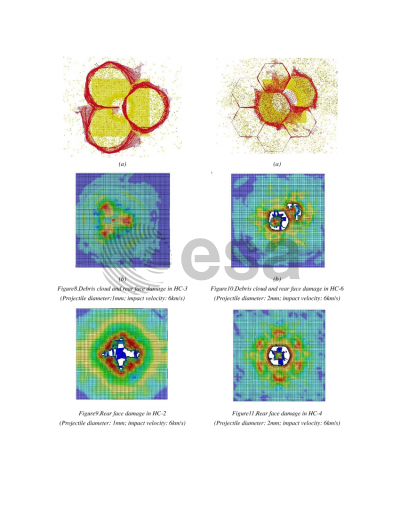
Document details

Abstract
To understand the process of hypervelocity impact on honeycomb sandwich panels, numerical simulation was carried out by using LS-DYNA hydrocode. The honeycomb panels were impacted by aluminum spheres of diameters ranging from 1mm to 2mm at velocity around 6km/s. Smooth Particle Hydrodynamic method was used coupling with finite element method. The projectile and front face sheet was modeled as SPH particles, while the rear face sheet was modeled as solid elements. Honeycomb cores were modeled as shell elements. It was shown that radial expanding of debris cloud was restricted by honeycomb cells. Additionally, honeycomb cores had considerable channeling and branching effects on debris cloud in the axial path. Further more, the location where projectiles impacted on the front face sheet had a significant influence on the damage of the rear face sheet. Test result that was obtained at Range A was described in this paper. The simulation result agreed well with the test result.
Preview