Document details

Abstract
The increasingly stringent deorbiting regulations across all space-faring nations emphasize the need for effective and reliable solutions to address post-mission satellite disposal. High Performance Space Structure Systems GmbH (HPS) has developed the ADEO family of drag sail systems, offering a passive, sustainable solution for satellite deorbiting by leveraging residual atmospheric drag in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). The ADEO family covers a range of sail sizes, from the compact ADEO-P (1.7 m²) to the expansive ADEO-L (25 m²), enabling tailored solutions for diverse satellite designs and missions.
The ADEO-N model, in particular, has demonstrated flight heritage, with its ADEO-N2 variant successfully deployed on board of D-Orbit’s ION Satellite Carrier in 2022. This mission has provided critical flight data and operational insights, marking a significant step in validating ADEO as one of the most advanced deorbiting solutions available today.
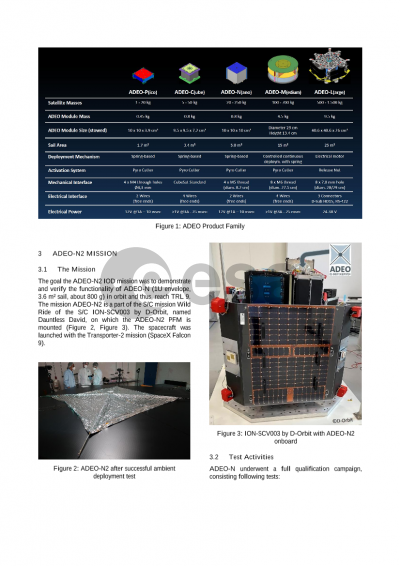
This paper focuses on the measurement results and lessons learned from the ADEO missions and other key activities across the ADEO product family. The onboard camera system captured the successful deployment of the 3.6 m² drag sail, while telemetry data has been continuously monitored to assess its performance. The results indicate effective deorbiting performance, demonstrating the system’s robust design and operational reliability. These findings contribute to growing confidence in ADEO’s role in advancing compliance with Zero Debris policies and requirements.
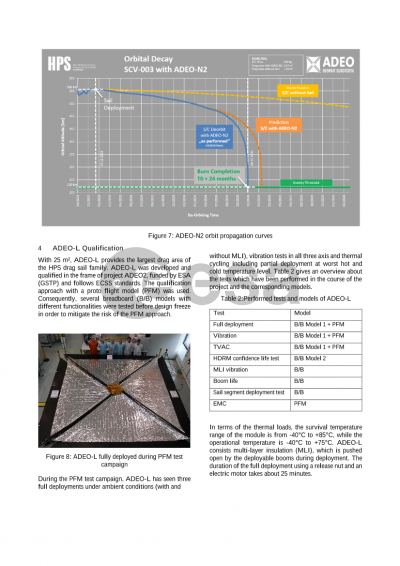
Beyond deorbiting, the ADEO system shows potential for broader applications, including the detection of space debris. This versatility underscores its value as a multi-functional tool for space sustainability. In December 2023, the ADEO-L completed its qualification campaign, paving the way for its integration on a host satellite in 2025. The experiences from the qualification and deployment processes of the ADEO-L and other models offer valuable insights for the future development and application of the technology.
The presentation will provide a comprehensive overview of ADEO’s in-flight performance, detailing the successes and challenges encountered. Topics will include deployment dynamics, drag efficiency, telemetry data analysis, and integration processes. Special attention will be given to the lessons learned from the ADEO-N2 mission, which serve as a foundation for continuous improvement and future innovations in drag sail technology.
By sharing these insights, we aim to contribute to the global dialogue on space debris mitigation and satellite end-of-life management. ADEO’s proven performance and expanding applications reaffirm its position as a key enabler for sustainable space operations. This paper highlights the importance of collaborative efforts and continuous advancements in addressing the critical challenge of maintaining a debris-free orbital environment.
Preview