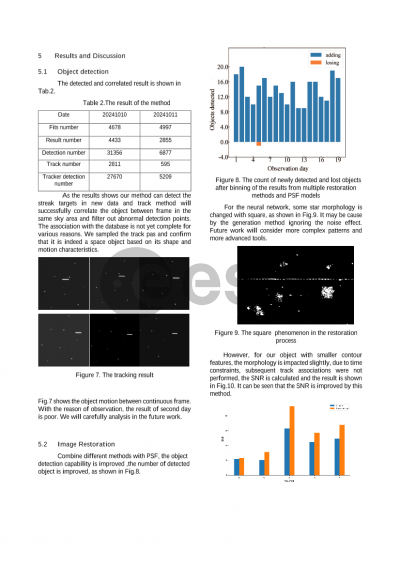
Document details

Abstract
The development of modern science and technology bring more and more satellite into earth orbit for navigation, communication or climate to benefit society. Nonetheless,this explosive growth in space object number also pose threat to the satellite operation and the development of space environment. It is imperative to implement necessary measures to ameliorate this situation. The first step is to achieve space situational awareness(SSA),which is the ability to detect, track, and understand objects in Earth’s orbit, including satellites and space debris this will be essential for safe, sustainable space operations and preventing collisions in a crowded orbit. Utilizing an optical telescope is an effective way to perform space debris surveys with the advantage of low-cost multi-dimensionality. Optical surveys using astronomical telescopes are an efficient way to observe and catalogue space debris, especially for detecting debris in medium or geostationary Earth orbits. Eliminating background star and the object candidate are detected by various of approach. With the new generation of device composed by multiple larger field of view telescope, the depth and breadth of the investigation have significantly increased, in the big data of 8K*8K image, which bring about minimal targets in wide fields, densely packed star fields difficult to detect, and other unpredictable issues, a data-based deep-learning method is proposed for detecting space object with high accuracy and speed. We select novel object detection neural network and optimize for our task. In order to improve the detection efficiency and robustness, several innovative algorithms are introduced to eliminate noise and increase the object detection ability, and the whole pipeline is optimized to reduce the raw images in real time. A trial survey with a wide field of view and small aperture telescope is presented to test our technique. In our survey, two observing strategies are adopted according to the dynamical features of space objects in the high Earth orbital region, and large numbers of raw CCD images are obtained for both strategies; the efficiency of our reduction is investigated based on the reduction results. Our technique exhibits a correlation rate higher than 97%, and around 400 objects can be routinely observed and catalogued just utilizing one wide field of view telescope in one night. On the experimental data of the new equipment with manually verification. Result show this artificial intelligence with great performance can be applie
Preview