Document details

Abstract
Space Surveillance and Tracking (SST) addresses detecting, cataloguing, and predicting objects orbiting the Earth, and the derived applications, such as conjunction prediction, re-entry prediction, and fragmentation analysis. SST technology development, test and validation represent one of the main areas in the Space Situational Awareness (SSA) Programme of ESA, which from 2020 has evolved into ESA's Space Safety Programme.
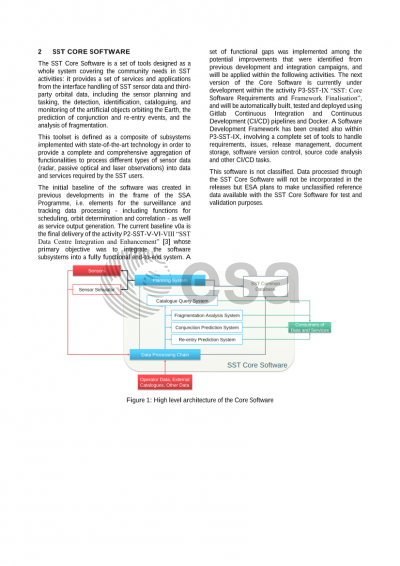
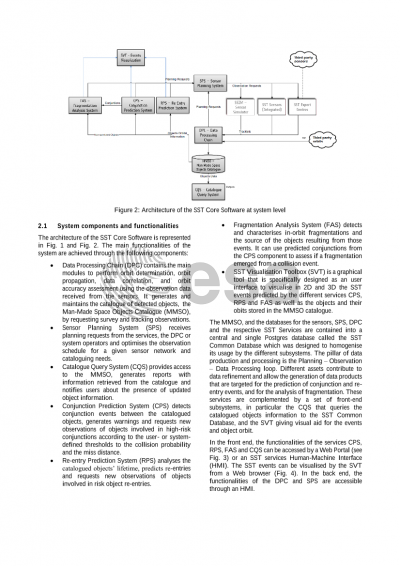
Since the start of the SSA Programme in 2009 the number of European activities has been growing significantly. Beside today’s dominant national and multi-national efforts to build-up and maintain object catalogues and to derive services, commercial endeavours are also starting. In support of the European partners ESA introduced the concept of a community approach towards an SST Core Software in 2017 as a key objective of the SSA and Space Safety programmes. The initial software baseline was created in previous developments in the SSA programme, i.e. elements for the surveillance data processing- including functions for scheduling, orbit determination and correlation- as well as service output generation. The community approach aims at supporting interoperability, compatibility and at minimising maintenance efforts for the participating national programmes in Europe.
The approach established the SST User Forum (SST-UF) as the community’s technical advisory body for the SST Core Software. As of now, ten ESA Member States participate with their national representatives to support the community, and the user forum has been meeting twice a year since November 2017.
The SST-UF plays a key role in providing guidance on all aspects of the software evolution, covering the identification and consolidation of requirements and their implementation. It also supports the governance and licensing approach and contributes to the standardisation efforts for SST data exchange formats. The user community in the SST-UF is therefore in the position to drive and control future releases of the software. It is also responsible for defining and managing the technical and organisational goals of the collaboration mechanism, including the workflows for the SST Core Software Development Framework.
Several activities are being conducted in the software development. The initial version of the Core Software (v0a) has been approved for licensing to the SST-UF members under ESA Community License in 2020. The next version of the Core Software is currently under development, and will be automatically built, tested and deployed using Gitlab CI/CD pipelines and Docker. A Software Development Framework has been created, which includes a complete set of tools to handle requirements, issues, release management, document storage, software version control, source code analysis and CI/CD tasks.
Additionally, a large set of testing data from optical, radar and satellite laser ranging sensors is being collected over a series of observation campaigns. Together with simulated data these resources are intended to support test and validation of the SST Core Software.
We here provide an overview of the community approach and the current status of the SST Core Software, outline the collaboration framework supporting the community through the SST-UF in the software development, maintenance and evolution, and report on the related workplan activities in ESA programmes.
Preview