Document details

Abstract
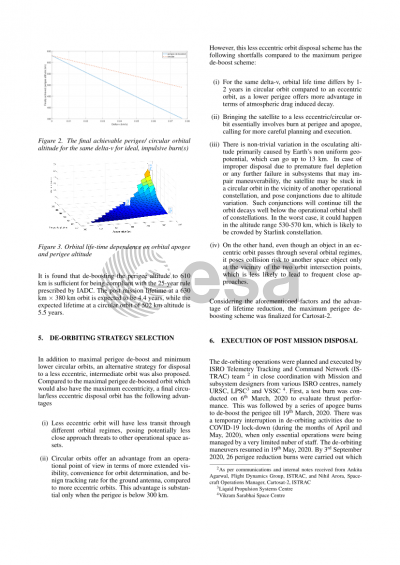
Cartosat-2 was launched on 10th January, 2007, with a planned mission life of 5 years. After providing uninterrupted payload services for 12 years, it was decided to decommission the satellite in late 2019 following on-board subsystem degradation. At an orbit of 630 km altitude, the lifetime of Cartosat-2 was estimated to be more than 30 years. The satellite also had about 26 kg left-over propellant. Although the satellite was not specifically designed for end-of-life de-orbiting, it was proposed by ISRO’s Directorate for Space Situational Awareness and Management (DSSAM) to lower the perigee of the satellite, so as to limit its post mission orbital life time in compliance with the 25-year guideline of IADC for post mission disposal of LEO objects, and at the same time, deplete the left-over fuel to mitigate any accidental break-up risk. The de-orbiting operations were planned and executed by the operational team at ISRO Telemetry Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in close coordination with Mission and subsystem designers from various ISRO centres. Starting with the first perigee-lowering manoeuvre on 6th March, 2020, 26 perigee reduction burns were conducted till 3rd September 2020 to progressively lower the perigee below 400 km, except for an interruption in the exercise during the months of April and May due to COVID-19 outbreak. Considering the variability due to solar flux and geomagnetic index affecting the atmospheric density, the life-time of the satellite in the currently achieved orbit (630 km x 390 km in size) is expected to be less than 10 years.
Cartosat-2 is the first LEO satellite where post mission disposal was carried out by ISRO, marking an important milestone towards compliance with the space debris mitigation guideline of UN/IADC concerning LEO objects. The disposal exercise provided invaluable experience and better insights into various operational aspects concerned with post mission disposal, which will be suitably leveraged in future for planning post mission disposal of similar LEO satellites. This paper outlines the background analyses and strategies that culminated in the successful de-orbiting of Cartosat-2.
Preview