Document details

Abstract
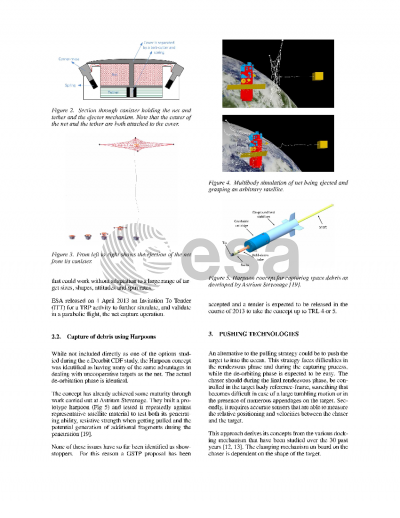
Space debris is an existing and growing problem for space operations. Studies show that for a continued use of LEO, 5 - 10 large and strategically chosen debris need to be removed every year. The European Space Agency (ESA) is actively pursuing technologies and systems for space debris removal under its Clean Space initiative. This overview paper describes the activities that are currently ongoing at ESA and that have already been completed. Additionally it outlines the plan for the near future. The technologies under study fall in two main categories corresponding to whether a pushing or a pulling manoeuvre is required for the de-orbitation. ESA is studying the option of using a tethered capture system for controlled de-orbitation through pulling where the capture is performed using throw-nets or alternatively a harpoon. The Agency is also studying rigid capture systems with a particular emphasis on tentacles (potentially combined with a robotic arm). Here the de-orbitation is achieved through a push-manoeuvre. Additionally, a number of activities will be discussed that are ongoing to develop supporting technologies for these scenarios, or to develop systems for de-orbiting debris that can be allowed to re-enter in an uncontrolled manner. The short term goal and main driver for the current technology developments is to achieve sufficient TRL on required technologies to support a potential de-orbitation mission to remove a large and strategically chosen piece of debris.
Preview