Document details

Abstract
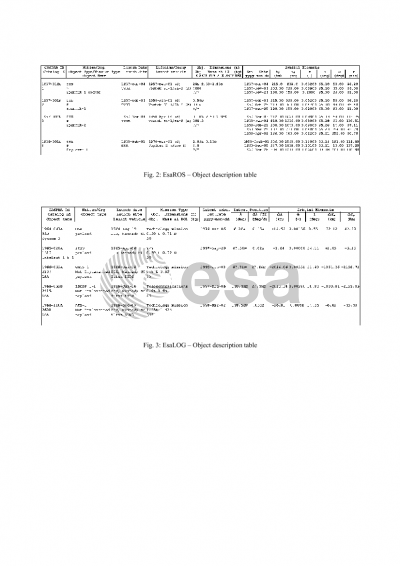
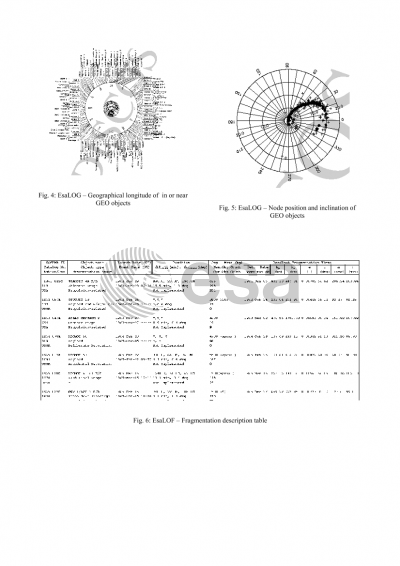
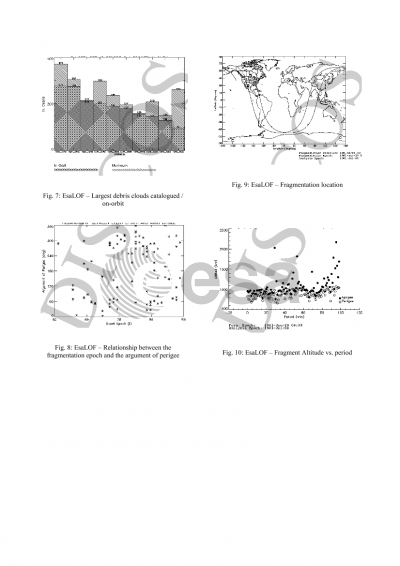
ESA's space debris database DISCOS-2 contains a wealth of information on the trackable Space Object Population between LEO and GEO altitudes, together with additional data on launches, launch sites, launchers, etc. These data has been recently made available through a Web Interface. But even with this new interface, two problems arise for potential users. First, users need to be familiarised with the tools provided by the DISCOS-2 Web Interface, in particular some knowledge of SQL is required in order to access the database contents. This problem is particularly important for occasional users of the database. Second, remote access using the Internet can be a boring, repetitive work, depending on the error frequency and workload of the net. Those two problems can make users to minimise the use of the database. To solve these problems, a DISCOS Space Data Publication and Documentation System (DISPAD) was created, aimed at easing the access to database data. The generation of periodical publications based on reports on the information in DISCOS-2 facilitates the distribution of such data to a wider range of users and represents a helpful complement to the interactive access to the database provided by the DISCOS-2 Web Interface. The DISPAD system produces regular situation reports on the DISCOS data contents and its implications with respect to orbit population evolution, development and launch policies, and spatial distribution of objects, on-orbit fragmentation, and effects of mitigation measures, such as GEO reorbiting. The DISPAD system is being implemented using the tools provided by the Oracle RDBMS, PV-Wave for graphical charts, Perl language for processing of the information extracted from the database, and LaTeX-2ε text processing system for production of the final form of the reports. Currently, GMV is updating the DISPAD system to adapt it to the new DISCOS-2 System, which includes a number of new tables and new data sources. As part of this update, new tables and graphical charts are being included in the reports, and a critical review of the already existing information is being performed. The newly created tables and charts follow the basic outline of the first release, but adapted to the new database scheme.
Preview