Document details

Abstract
The satellite laser ranging station Graz is currently involved in many different space debris related projects and experiments. Besides the presentation of technological improvements the talk will focus on attitude determination and observation strategies.
FLOAT: The new space debris laser in Graz is mounted directly on the telescope avoiding any Coudé path. Besides easier alignment and usability such an approach provides a method of upgrading existing SLR or astronomy telescopes.
Light curves: In addition and simultaneous to SLR light curves are recorded utilizing single photon avalanche detectors with up to 10 µs temporal resolution.
Stare and chase: An approach is presented allowing the observation of low earth orbit objects, pointing determination, orbit determination and space debris laser ranging within a single pass.
Expert center: The second phase of the expert coordination center includes an approach to validate and qualify SLR stations for active and passive space debris measurements. In addition to that multi-static experiments will be conducted.
Technosat: Within an experimental mission of the Technical University of Munich the satellite Technosat was equipped with commercial off the shelf retroreflectors. An optimal arrangement (which was simulated and verified experimentally with ground based methods) allows precise attitude determination using kHz SLR techniques.
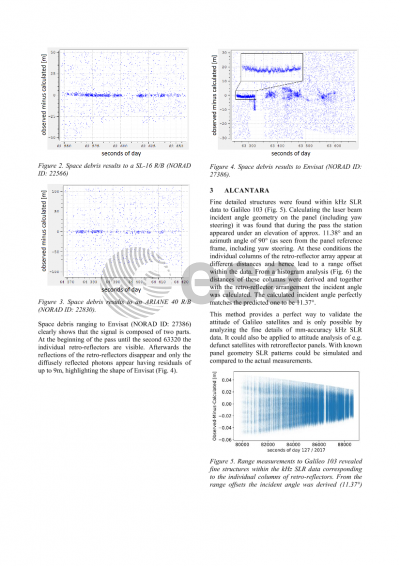
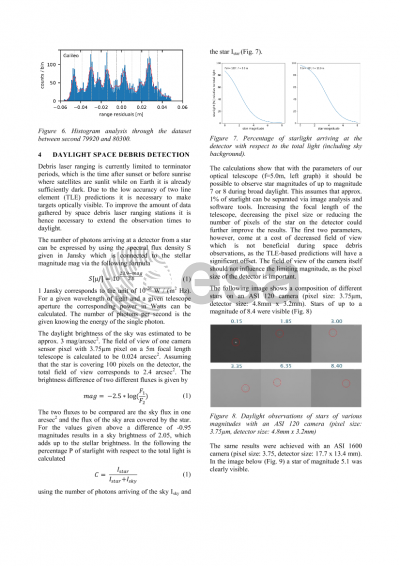
Alcantara: A method of the attitude determination of satellites equipped with retroreflector panels is presented investigating fine reflection patterns appearing within the kHz SLR data.
Preview