Document details

Abstract
A central tenet of space safety and sustainability is that of data portals and employment of data exchange using standardized data formats and exchange mechanisms. The new Spacebook portal, https://spacebook.com/, is an internet-based service that is designed to provide global access to essential space situational awareness (SSA) data that spacecraft owners, operators, SSA centers, and academia need to inform their operations and activities.
The paper gives an overview of the key constituents of the Spacebook portal, including: (1) a highly performant, Cesium-based space population “Explorer;” (2) space weather; (3) Earth orientation parameters; (4) a synthetic covariance information; (5) a comparative SSA “live” analyses; (6) XP-TLEs fitted to all public objects in the SP High-Accuracy Catalog; (7) a technical library of COMSPOC-authored content; (8) a technical video library; (9) a Rendezvous and Proximity Operations (RPO) analysis section; (10) reference orbits and comparisons with a variety of SSA positional knowledge products; (11) a download portal with APIs to obtain and interact with content; and (12) a space standards informational tab and with reference links.
The paper will describe how to obtain space weather and Earth Orientation Parameters (EOP) data under the “Downloads” tab, with options for obtaining “full” or “recent” data sets.
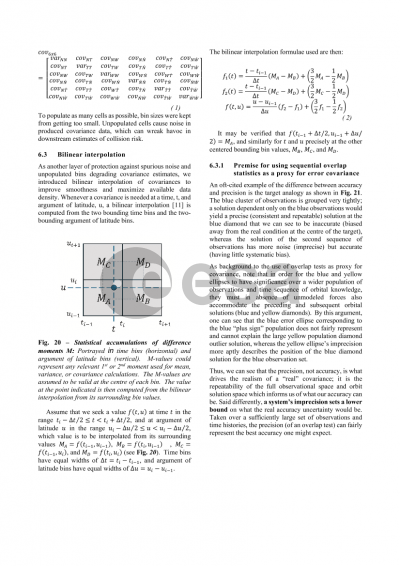
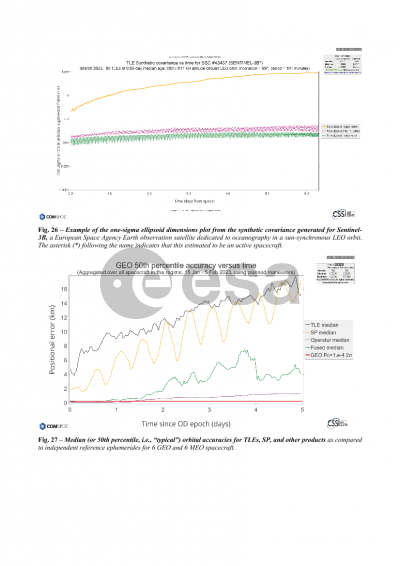
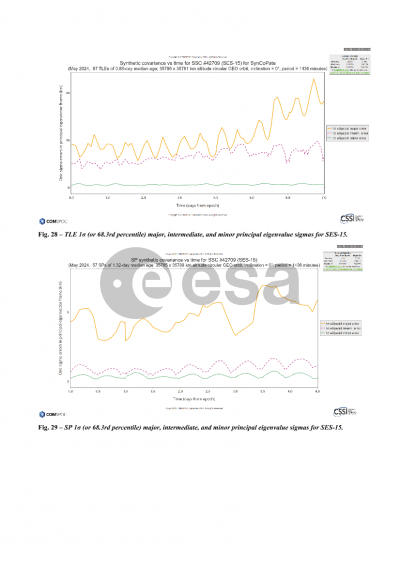
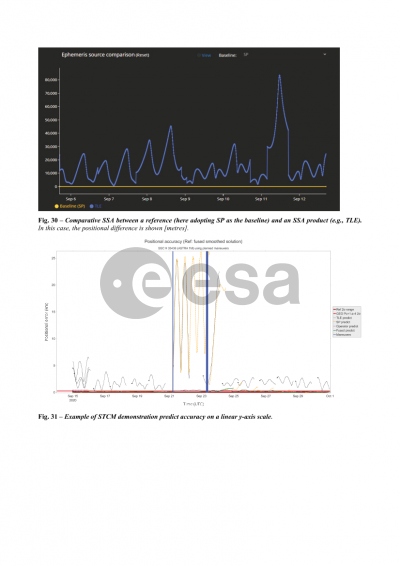
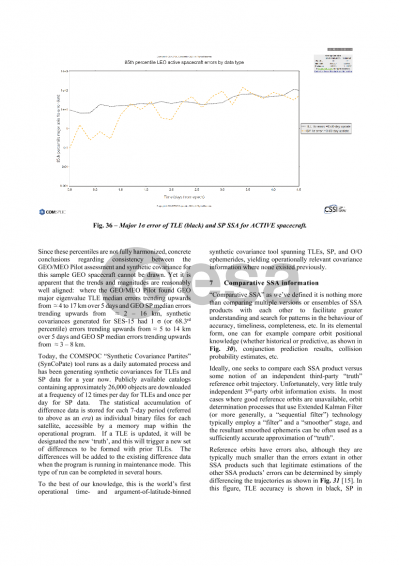
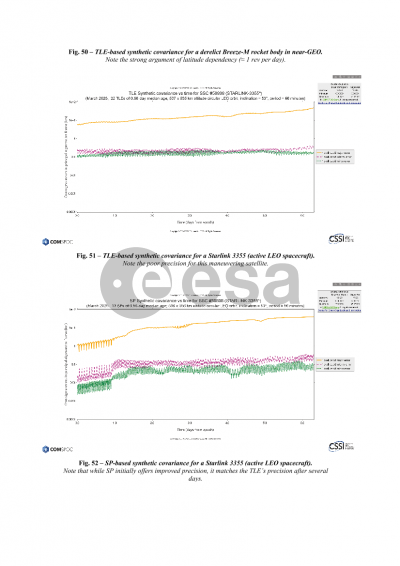
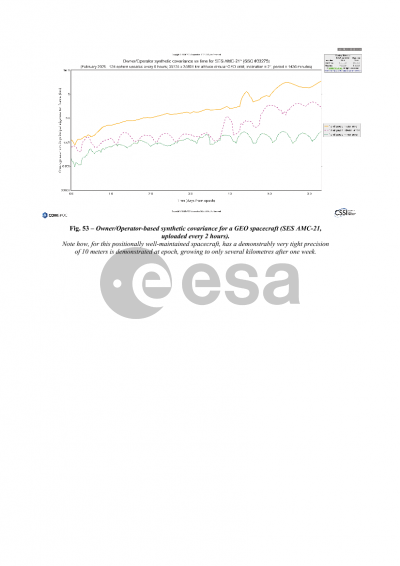
Synthetic covariances are described next. Positional covariances are required to do an assessment of collision probability, yet often times such covariances are either not available or not typically provided. Synthetic covariances offer a workaround for such cases. Spacebook provides a new digital statistics approach to 6x6 covariance uncertainty modeling that eliminates the need to assume a priori time-varying error functions for all error components and their correlations, with statistics drawn from within time and argument-of-latitude bins on an object-by-object basis. Downloads of synthetic covariances take the form of TLE-based full ephemeris files containing covariance information, Plotly files of TLE-based synthetic covariance sigmas, and Plotly files of SP ephemeris-derived synthetic covariance sigmas for all objects in the public space catalog.
SGP4-XP represents a new propagator available to the public through the United States Space Force (USSF) dynamic link library (.DLL) on the Space-Track.org website. SGP4-XP is a new semi analytical theory that replaces the previous SGP4 theory with more realistic force models better-suited for all orbital regimes, with up to tenfold accuracy improvements particularly in the orbital regimes above LEO. Spacebook converts ephemerides (obtained from any source) to SGP4-XP TLEs via a simple differential correction scheme. Users having the USSF SGP4-XP software DLL library may find these SGP4-XP TLEs useful for routine operations.
The technical videos card links to COMSPOC’s website, to a page that contains videos produced by COMSPOC’s research and operations teams. These videos show recent events that have happened in space, modeling and predictions of potential threats, as well as the results of research studies.
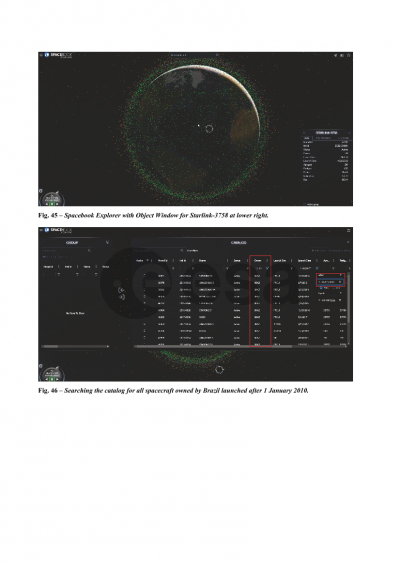
The Spacebook Explorer is a highly performant Cesium-based 3D visualization engine with which you can see what is currently happening in space. The default explorer window shows all space objects in the current Spacebook catalog. Each dot represents a space object and is colored according to the following default scheme: (a) Active satellites – green; (b) Rocket bodies – red; (c) Inactive satellites – yellow; (d) Debris – gray; and (e) Unknown – white. New Cesium capabilities to depict spatial density of the space catalog are included.
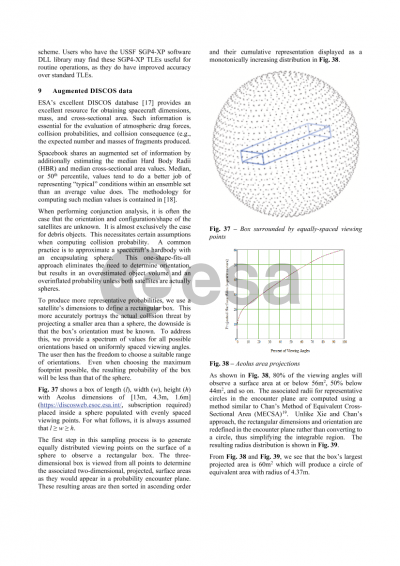
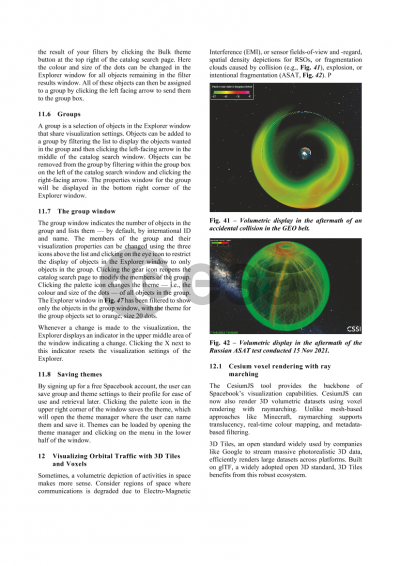
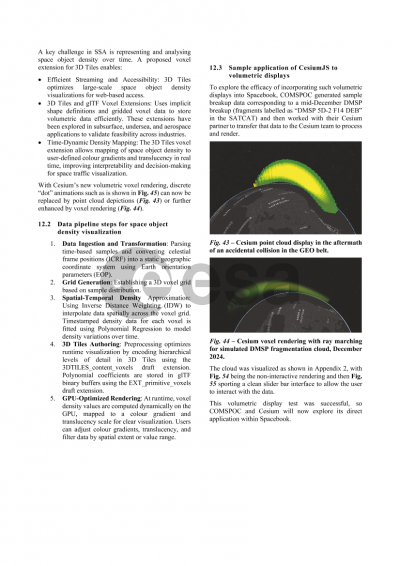
The core functionality of Spacebook is the ability to download space data to use in your own missions or applications. There are two ways to download data: through the user interface or through the API. Users can run bulk downloads for TLE, space weather, EOP, and satellite catalog files. To download a bulk set of data, click one of the options on the right side of the window in that row. Synthetic covariance and XP-TLEs for any public space object can also be downloaded, even for a filtered list of satellites. Some objects also have reference ephemeris, which you can download if the download icon is shown under the reference ephemeris column for that object.
Preview